About Your Seat Belts
Seat belts are the single most effective safety device because they keep you connected to the vehicle so that you can take advantage of many built-in safety features. They also help to keep you from being thrown against the inside of the vehicle, against any passengers, or out of the vehicle. When worn properly, seat belts also keep your body properly positioned in a crash so that you can take full advantage of the additional protection provided by the airbags.
Lap/shoulder seat belts
All four seating positions are equipped with lap/shoulder seat belts with emergency locking retractors. In normal driving, the retractor lets you move freely while keeping some tension on the belt. During a collision or sudden stop, the retractor locks to restrain your body.
The seat belt must be properly secured when using a front-facing child restraint system.
In addition, seat belts help to protect you in almost every type of crash, including:
- frontal impacts
- side impacts
- rear impacts
- rollovers
Seat belts cannot completely protect you in every crash. But in most cases, seat belts can reduce your risk of serious injury.
Most countries require you to wear seat belts. Take time to familiarise with the legal requirements of the countries in which you will drive.
 WARNING
WARNING
Not wearing a seat belt properly increases the chance of serious injury or death in a crash, even though your vehicle has airbags.
Be sure you and your passengers always wear seat belts and wear them properly.
WARNING: Seat belts are designed to bear upon the bony structure of the body, and should be worn low across the front of the pelvis or the pelvis, chest and shoulders, as applicable; wearing the lap section of the belt across the abdominal area must be avoided.
WARNING: Seat belts should be adjusted as firmly as possible, consistent with comfort, to provide the protection for which they have been designed. A slack belt will greatly reduce the protection afforded to the wearer.
WARNING: Belts should not be worn with straps twisted.
WARNING: Each belt assembly must only be used by one occupant; it is dangerous to put a belt around a child being carried on the occupant’s lap.

- All occupants should sit upright, well back in the seat, and remain in that position for the duration of the trip. Slouching and leaning reduce the effectiveness of the belt and can increase the chance of serious injury in a crash.
- Never place the shoulder part of a lap/shoulder seat belt under your arm or behind your back. This could cause very serious injuries in a crash.
- Two people should never use the same seat belt. If they do, they could be very seriously injured in a crash.
- Do not put any accessories on the seat belts. Devices intended to improve comfort or reposition the shoulder part of a seat belt can reduce the protective capability and increase the chance of serious injury in a crash.

Seat Belt Reminder
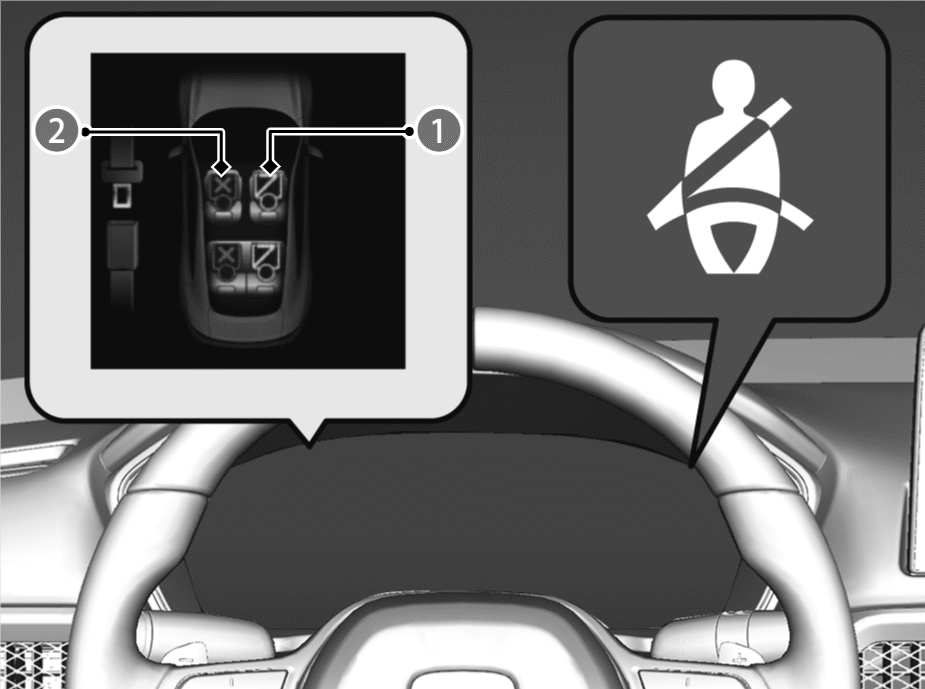

Fastened

Unfastened
The seat belt reminder informs you that the occupant’s seat belt is not being fastened. The warning will disappear when you wear your seat belt.
When driving with an unfastened seat belt, the buzzer will stop when the vehicle is stopped or a certain period of time has passed.
- Even when no one is sitting in the front passenger seat, the system may react if luggage is placed on the seat.
- The system may not react if a child or small person is seated in the front passenger seat, or if a cushion is being used.
If none of these conditions exist, have your vehicle checked by a dealer.
Automatic Seat Belt Tensioners
The front seats are equipped with automatic seat belt tensioners to enhance safety.
The tensioners automatically tighten the front seat belts during a moderate-to-severe frontal or side collision, sometimes even if the collision is not severe enough to inflate the front airbags or the driver's and passenger's knee airbag.
The seat belt tensioners can only operate once. If a tensioner is activated, the SRS indicator will come on. Have a dealer replace the tensioner and thoroughly inspect the seat belt system as it may not offer protection in a subsequent crash.
